Intro to iteration with Base R
Daniel Anderson
Week 2, Class 1
Basic overview: for loops
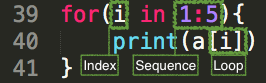
a <- letters[1:26]a## [1] "a" "b" "c" "d" "e" "f" "g" "h" "i" "j" "k" "l" "m" "n" "o" "p" "q" "r" "s" "t" "u"## [22] "v" "w" "x" "y" "z"for(i in 1:5){ print(a[i])}## [1] "a"## [1] "b"## [1] "c"## [1] "d"## [1] "e"Note these are five different character scalars (atomic vectors of length one). It is NOT a single vector.
Running the loop
for(i in 1:length(x)) { print(letters[i])}## [1] "a"## character(0)for(i in seq_along(x)) { print(letters[i])}The first may return unhelpful error messages or unexpected output, while the latter simply won't run, which is generally easier to diagnose.
Even better, if you're using a loop in a function, you should probably have a condition that checks the input before running it
Another example
Say we wanted to simulate 100 cases from random normal data, where we varied the standard deviation in increments of 0.2, ranging from 1 to 5
First, specify a vector standard deviations
increments <- seq(1, 5, by = 0.2)- Next, allocate a vector. There are many ways I could store this result (data frame, matrix, list). I'll do it in a list.
simulated <- vector("list", length(increments))str(simulated)## List of 21## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULL## $ : NULLWrite for loop
for(i in seq_along(simulated)) { simulated[[i]] <- rnorm(100, 0, increments[i]) # note use of `[[` above}str(simulated)## List of 21## $ : num [1:100] -2.387 0.405 -1.599 -0.285 0.288 ...## $ : num [1:100] 0.298 0.433 -1.021 1.384 -0.323 ...## $ : num [1:100] 0.893 -1.799 -0.819 -1.11 -2.198 ...## $ : num [1:100] -0.332 1.067 -0.823 2.899 1.863 ...## $ : num [1:100] -2.568 -0.672 -0.244 -1.645 2.221 ...## $ : num [1:100] 2.4 -1.95 1.13 3.05 3.56 ...## $ : num [1:100] -2.978 0.798 2.212 2.15 -2.197 ...## $ : num [1:100] -0.211 -1.768 3.35 2.06 0.213 ...## $ : num [1:100] 0.718 -4.029 -1.093 0.417 -3.952 ...## $ : num [1:100] 0.632 3.084 -2.62 -1.282 -2.965 ...## $ : num [1:100] 2.1759 -0.4681 1.6349 -0.0809 -0.7611 ...## $ : num [1:100] 1.236 3.055 -2.575 -0.868 4.369 ...## $ : num [1:100] 0.7795 -1.0125 -6.465 0.0926 1.8629 ...## $ : num [1:100] 3.466 -1.245 0.496 3.67 -2.207 ...## $ : num [1:100] -2.712 -4.21 -3.686 -0.728 -0.142 ...## $ : num [1:100] 2.83 6.08 -3 4.29 4.18 ...## $ : num [1:100] 0.335 0.574 4.106 4.414 0.897 ...## $ : num [1:100] -2.123 3.165 1.104 -4.065 0.578 ...## $ : num [1:100] 2.448 -1.472 4.411 2.34 -0.346 ...## $ : num [1:100] 0.672 -4.724 3.378 -1.811 10.33 ...## $ : num [1:100] -3.46 2.83 -11.49 -1.86 7.54 ...List/data frame
Remember, if all the vectors of our list are the same length, it can be transformed into a data frame.
First, let's provide meaningful names
names(simulated) <- paste0("sd_", increments)sim_d <- data.frame(simulated)head(sim_d)## sd_1 sd_1.2 sd_1.4 sd_1.6 sd_1.8 sd_2 sd_2.2## 1 -2.3872613 0.2979273 0.8930471 -0.3319310 -2.5676229 2.3954045 -2.9775420## 2 0.4051212 0.4329239 -1.7989656 1.0673114 -0.6722755 -1.9542566 0.7980123## 3 -1.5992856 -1.0209222 -0.8192303 -0.8232251 -0.2435614 1.1309855 2.2118028## 4 -0.2847246 1.3838266 -1.1097486 2.8991565 -1.6445420 3.0545722 2.1497809## 5 0.2881735 -0.3233308 -2.1982580 1.8633398 2.2213515 3.5578607 -2.1969056## 6 0.1175257 -0.4150724 0.6353818 0.7142314 -0.5219616 -0.8029945 0.1464460## sd_2.4 sd_2.6 sd_2.8 sd_3 sd_3.2 sd_3.4 sd_3.6## 1 -0.2105980 0.7175135 0.6321448 2.17589282 1.2362364 0.77947966 3.4658329## 2 -1.7675364 -4.0290962 3.0843027 -0.46812673 3.0554725 -1.01245886 -1.2451870## 3 3.3501949 -1.0927053 -2.6196216 1.63492841 -2.5751022 -6.46499466 0.4960868## 4 2.0601974 0.4174713 -1.2824915 -0.08085208 -0.8678742 0.09259855 3.6701383## 5 0.2125117 -3.9521276 -2.9646399 -0.76111234 4.3687915 1.86290325 -2.2067855## 6 1.7822910 -0.1081454 4.5420524 3.53122922 -2.4194781 -1.14660593 -1.7557261## sd_3.8 sd_4 sd_4.2 sd_4.4 sd_4.6 sd_4.8 sd_5## 1 -2.7119876 2.834307 0.3347596 -2.122876 2.4479578 0.6723229 -3.464762## 2 -4.2104097 6.083823 0.5735697 3.164909 -1.4721622 -4.7240885 2.825094## 3 -3.6861183 -3.000288 4.1063037 1.104068 4.4111688 3.3779921 -11.486532## 4 -0.7277885 4.293730 4.4141833 -4.064636 2.3400425 -1.8110032 -1.857547## 5 -0.1416683 4.178344 0.8965279 0.578414 -0.3461786 10.3301558 7.544994## 6 -2.2110984 4.644032 -5.7370545 -5.072939 4.7260451 0.4489877 2.956989tidyverse
- One of the best things about the tidyverse is that it often does the looping for you
library(tidyverse)pd <- sim_d %>% pivot_longer( everything(), names_to = "sd", values_to = "sim", names_prefix = "sd_", names_ptypes = list( sd = factor() ) ) ggplot(pd, aes(sim)) + geom_density( aes(color = sd) ) + guides(color = "none")
Base R Method
- Calculate all the densities
densities <- vector("list", length(sim_d))for(i in seq_along(densities)) { densities[[i]] <- density(sim_d[ ,i])}str(densities)## List of 21## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -3.45 -3.44 -3.42 -3.41 -3.4 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 0.000173 0.000195 0.000219 0.000245 0.000274 ...## ..$ bw : num 0.355## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -3.39 -3.38 -3.36 -3.35 -3.33 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 0.000261 0.000296 0.000334 0.000377 0.000425 ...## ..$ bw : num 0.405## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -4.9 -4.88 -4.87 -4.85 -4.83 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 9.72e-05 1.09e-04 1.22e-04 1.37e-04 1.53e-04 ...## ..$ bw : num 0.495## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -5.64 -5.62 -5.59 -5.57 -5.54 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 0.000132 0.00015 0.000171 0.000195 0.000221 ...## ..$ bw : num 0.572## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -5.97 -5.95 -5.92 -5.9 -5.88 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 0.00012 0.000137 0.000155 0.000175 0.000198 ...## ..$ bw : num 0.559## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -5.57 -5.55 -5.53 -5.5 -5.48 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 0.000137 0.000153 0.000169 0.000187 0.000207 ...## ..$ bw : num 0.698## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -7.7 -7.67 -7.64 -7.61 -7.58 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 5.93e-05 6.65e-05 7.46e-05 8.37e-05 9.35e-05 ...## ..$ bw : num 0.768## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -9.48 -9.44 -9.4 -9.37 -9.33 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 5.38e-05 6.18e-05 7.07e-05 8.06e-05 9.17e-05 ...## ..$ bw : num 0.834## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -9.05 -9.02 -8.98 -8.95 -8.91 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 5.98e-05 6.80e-05 7.71e-05 8.74e-05 9.91e-05 ...## ..$ bw : num 0.813## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -9.05 -9.02 -8.99 -8.95 -8.92 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 6.33e-05 7.07e-05 7.87e-05 8.79e-05 9.79e-05 ...## ..$ bw : num 0.954## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -9.69 -9.65 -9.61 -9.57 -9.54 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 0.000107 0.00012 0.000135 0.000151 0.000169 ...## ..$ bw : num 1.08## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -9.73 -9.69 -9.64 -9.6 -9.56 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 9.15e-05 1.03e-04 1.15e-04 1.29e-04 1.44e-04 ...## ..$ bw : num 1.12## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -11.3 -11.2 -11.2 -11.2 -11.1 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 4.55e-05 5.14e-05 5.79e-05 6.53e-05 7.34e-05 ...## ..$ bw : num 0.989## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -12 -11.9 -11.9 -11.8 -11.8 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 4.34e-05 4.86e-05 5.45e-05 6.09e-05 6.78e-05 ...## ..$ bw : num 1.04## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -11 -10.9 -10.9 -10.9 -10.8 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 7.10e-05 7.95e-05 8.87e-05 9.88e-05 1.10e-04 ...## ..$ bw : num 1.18## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -11.6 -11.5 -11.5 -11.4 -11.4 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 6.28e-05 7.04e-05 7.89e-05 8.84e-05 9.87e-05 ...## ..$ bw : num 1.3## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -15 -15 -14.9 -14.9 -14.8 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 3.18e-05 3.64e-05 4.14e-05 4.70e-05 5.32e-05 ...## ..$ bw : num 1.41## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -13.9 -13.9 -13.8 -13.8 -13.7 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 6.35e-05 7.18e-05 8.15e-05 9.22e-05 1.04e-04 ...## ..$ bw : num 1.4## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -15.6 -15.5 -15.5 -15.4 -15.4 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 3.11e-05 3.48e-05 3.88e-05 4.33e-05 4.83e-05 ...## ..$ bw : num 1.48## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -14 -13.9 -13.9 -13.8 -13.7 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 4.97e-05 5.57e-05 6.26e-05 7.01e-05 7.83e-05 ...## ..$ bw : num 1.78## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"## $ :List of 7## ..$ x : num [1:512] -17.4 -17.3 -17.2 -17.2 -17.1 ...## ..$ y : num [1:512] 3.78e-05 4.25e-05 4.76e-05 5.34e-05 5.98e-05 ...## ..$ bw : num 1.71## ..$ n : int 100## ..$ call : language density.default(x = sim_d[, i])## ..$ data.name: chr "sim_d[, i]"## ..$ has.na : logi FALSE## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "density"Skipping iterations
- On the prior slide, I set the index to skip over the first by using
seq(2, length(densities)) - Alternatively, the loop could have been written like this
plot(densities[[1]], xlim = c(-20, 20))for(i in seq_along(densities)) { if(i == 1) next lines(x = densities[[i]]$x, y = densities[[i]]$y) }
Breaking loops
- Similarly, if a condition is met, you may want to break out of the loop
set.seed(1)rand_unif <- vector("double", 10)for(i in seq_along(rand_unif)) { rand_unif[i] <- runif(1, 0, 10) if(any(rand_unif > 5)) { break }}rand_unif## [1] 2.655087 3.721239 5.728534 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000## [10] 0.000000lapply
One of numerous functionals in R
A functional "takes a function as an input and returns a vector as output" (adv-r, Chpt 9)
lapply
One of numerous functionals in R
A functional "takes a function as an input and returns a vector as output" (adv-r, Chpt 9)
lapplywill always return a list
Revisiting our simulation with n=10
Our for loop version
increments <- seq(1, 5, by = 0.2)simulated <- vector("list", length(increments))for(i in seq_along(simulated)) { simulated[[i]] <- rnorm(10, 0, increments[i]) # note use of `[[`}simulated## [[1]]## [1] 1.329799263 1.272429321 0.414641434 -1.539950042 -0.928567035 -0.294720447## [7] -0.005767173 2.404653389 0.763593461 -0.799009249## ## [[2]]## [1] -1.3771884 -0.3473539 -0.3590581 -0.4938130 0.3026681 -1.0703054 0.5228200## [8] -1.4850461 -0.2691215 0.4528748## ## [[3]]## [1] 0.18667091 1.12586531 -0.07994948 0.70505116 1.52007711 -0.96733538 -1.79843910## [8] 0.06541664 -0.32998918 -0.76004356## ## [[4]]## [1] -0.6932965 -1.0391546 1.1628012 1.8430588 1.5874566 -0.6872210 1.9812866## [8] -0.4469541 2.8126449 0.8971937## ## [[5]]## [1] -0.8150112 -1.4976779 -2.0998270 -1.9180630 -2.8148077 2.0817666 1.4976848## [8] -0.4091916 0.4790473 -0.6780649## ## [[6]]## [1] 4.88272926 -1.59067823 -0.10975495 0.50028265 1.23648659 -0.34524701 -4.44780055## [8] -2.52722877 0.71745779 -0.02209096## ## [[7]]## [1] -2.06942816 -0.25481571 -1.79293116 0.53297966 -3.13521647 0.80507047 0.54650783## [8] 0.14363400 0.04214406 0.56614443## ## [[8]]## [1] -1.5576242 -0.2860050 1.5939257 2.6423258 0.3450516 -0.2826086 -2.1889641## [8] -3.4502070 -1.9130149 3.0097995## ## [[9]]## [1] 2.0075697 -0.5707406 -1.1045067 -1.0893483 2.5921658 -0.7170229 3.2656489## [8] 1.6813534 3.3782120 -2.2704815## ## [[10]]## [1] 0.02343869 -2.46644083 1.66952525 0.33520940 -0.79008686 4.07676752 0.64125485## [8] 2.79032300 2.18920572 -2.17497454## ## [[11]]## [1] -1.8479697 0.1397409 -3.3911573 1.7301563 -3.8422483 4.8763419 -1.5020898## [8] 5.0348916 -1.2375597 -2.9168605## ## [[12]]## [1] 0.08122518 0.08792107 -5.37658471 3.37200276 -3.58271713 1.07397507 1.58334645## [8] 0.44176867 -0.38013448 0.63258964## ## [[13]]## [1] -3.63355522 -2.73092494 -3.78680146 5.37231172 5.09258379 0.89299456 -4.19186408## [8] -0.01266001 5.13968576 -1.61737417## ## [[14]]## [1] 2.8724992 -3.5064092 2.4817417 -3.4410208 -4.4341454 -3.4448108 -3.1312183## [8] -3.2784505 2.6685947 0.2466415## ## [[15]]## [1] -1.230253 -4.128712 -3.860530 -2.917603 -4.254936 -1.703062 1.792598 -4.485865## [9] 5.586977 -4.983398## ## [[16]]## [1] -0.38609969 9.47887963 3.56250591 -1.00873265 -3.46305502 2.33034400 -0.05011739## [8] -1.49941905 1.27154294 -1.95522254## ## [[17]]## [1] 11.166364 7.057168 3.274253 2.995610 -2.280104 3.720269 -1.464098 -4.233829## [9] 7.909367 -3.901679## ## [[18]]## [1] -1.2944644 -2.7057812 -4.1671335 2.6354907 -6.7039055 -0.9072316 -2.5268998## [8] -6.1167306 -0.3098365 -1.8958699## ## [[19]]## [1] -2.72423672 4.51313434 2.44908304 -0.41609817 0.71985626 -3.39163378 -0.92616955## [8] 5.07001234 -0.07704198 0.74422771## ## [[20]]## [1] 9.71885467 -3.37773242 4.61180344 8.59432826 -5.10799278 0.08465542 -1.87156142## [8] -2.35599721 -5.01944473 -4.30181407## ## [[21]]## [1] 6.3469358 2.9692047 3.8781716 7.7868519 -1.8270090 4.0827822 -0.3031739## [8] -2.5068916 4.6303136 0.1846885The lapply version
increments <- seq(1, 5, by = 0.2)sim_l <- lapply(increments, function(sd) rnorm(10, 0, sd))sim_l## [[1]]## [1] -1.06620017 -0.23845635 1.49522344 1.17215855 -1.45770721 0.09505623 0.84766496## [8] -1.62436453 1.40856336 -0.54176036## ## [[2]]## [1] 0.33439767 -0.23276729 1.89138982 -1.77065716 -0.17352985 -1.14384377 0.48785128## [8] 2.67511464 -1.81739641 -0.07404891## ## [[3]]## [1] -0.2061791 2.1582303 -1.3745979 0.6952094 2.3757270 -0.3650308 -0.9883000## [8] -0.2256499 0.7018506 -1.4189555## ## [[4]]## [1] 2.583603577 0.009027176 -4.647838497 -1.771463710 2.476107092 -1.562928561## [7] -0.162405516 0.068240400 -2.554748823 0.785547796## ## [[5]]## [1] 0.7588861 3.3730270 1.8621258 0.1472586 -0.1485428 1.0909322 -1.5973563## [8] 0.1897585 0.6351741 0.9907080## ## [[6]]## [1] -2.2686619 2.9247031 1.4042334 5.0142223 -3.7800543 -1.1796256 -3.4290046## [8] -0.8419958 0.6202828 3.4051412## ## [[7]]## [1] -0.9754466 -2.6369136 -0.6762380 1.3663192 0.4001848 2.9004820 -0.6576005## [8] -3.6260878 2.0932966 -2.4488705## ## [[8]]## [1] 1.4807195 1.2323849 0.8867018 4.1373459 -0.4947470 -3.1540683 0.1523378## [8] -0.5567459 1.5241448 3.9231463## ## [[9]]## [1] -4.7016517 -0.5561035 0.1829520 1.4292399 -1.8117412 1.0154715 0.9916693## [8] -0.0321692 -0.3235310 3.8135359## ## [[10]]## [1] 1.8870003 5.4779907 -0.7533148 -3.4847443 -1.1079682 0.2727106 -0.6674835## [8] -1.1531183 -4.4162105 -2.2323731## ## [[11]]## [1] -3.2887103 0.9249262 1.0343854 4.6189443 -0.9885426 2.8451681 -1.4377668## [8] -4.5446604 1.3036100 -1.5586100## ## [[12]]## [1] -2.6705889 -2.4212723 3.4864112 5.0317853 3.2235660 -0.8741056 -4.1909745## [8] 0.7122363 3.5629862 2.6796621## ## [[13]]## [1] 1.0693570 0.7555414 -2.8682923 1.5089381 0.1897102 0.2311061 -0.6866699## [8] -3.9372519 -2.0153271 2.6046223## ## [[14]]## [1] 0.14014122 0.05272852 -0.67074108 5.04212698 0.06654805 0.89710564 0.53719465## [8] -3.46763945 -0.23928039 4.63291935## ## [[15]]## [1] 1.7408760 -5.5177075 0.2939007 2.1276020 -0.2847970 2.9742513 -0.6561405## [8] -3.9949164 2.7719149 0.9981279## ## [[16]]## [1] 2.1746314 4.1642412 0.7900246 -6.5183131 0.4841609 -6.5496878 -2.1241724## [8] 3.8147192 -6.8826026 0.4252825## ## [[17]]## [1] -2.5564077 -1.2650273 4.1000506 1.9152364 5.4365139 -4.7594493 -3.6517335## [8] -3.1708752 -0.5444685 -4.2075656## ## [[18]]## [1] -3.6074204 -4.2880309 2.6589614 2.4146654 4.0323037 11.7108920 -0.7931311## [8] 3.0140650 14.3722239 2.4666420## ## [[19]]## [1] -0.3174796 -4.4732375 -2.5142983 -7.7679847 -7.2329144 -1.8629409 1.4687175## [8] 0.1859673 -1.7940440 -8.3684223## ## [[20]]## [1] 3.1640674 2.2061840 7.7598064 -8.9097144 -1.3767546 8.4015451 0.5587853## [8] 6.6444152 2.7562604 0.6551559## ## [[21]]## [1] 4.57107994 -9.00413159 -1.69940320 3.03132286 6.70565155 3.83643644 0.96862833## [8] 5.70283345 0.06932402 -5.52652955Some more examples
Loop through a data frame
- Remember - a data frame is a list. We can loop through it easily
library(palmerpenguins)lapply(penguins, is.double)## $species## [1] FALSE## ## $island## [1] FALSE## ## $bill_length_mm## [1] TRUE## ## $bill_depth_mm## [1] TRUE## ## $flipper_length_mm## [1] FALSE## ## $body_mass_g## [1] FALSE## ## $sex## [1] FALSE## ## $year## [1] FALSEAdd a condition
lapply(penguins, function(x) { if(is.numeric(x)) { mean(x, na.rm = TRUE) }})## $species## NULL## ## $island## NULL## ## $bill_length_mm## [1] 43.92193## ## $bill_depth_mm## [1] 17.15117## ## $flipper_length_mm## [1] 200.9152## ## $body_mass_g## [1] 4201.754## ## $sex## NULL## ## $year## [1] 2008.029Add a second condition
lapply(penguins, function(x) { if(is.numeric(x)) { return(mean(x, na.rm = TRUE)) } else if(is.character(x) | is.factor(x)) { return(table(x)) }})## $species## x## Adelie Chinstrap Gentoo ## 152 68 124 ## ## $island## x## Biscoe Dream Torgersen ## 168 124 52 ## ## $bill_length_mm## [1] 43.92193## ## $bill_depth_mm## [1] 17.15117## ## $flipper_length_mm## [1] 200.9152## ## $body_mass_g## [1] 4201.754## ## $sex## x## female male ## 165 168 ## ## $year## [1] 2008.029Passing arguments
head(airquality)## Ozone Solar.R Wind Temp Month Day## 1 41 190 7.4 67 5 1## 2 36 118 8.0 72 5 2## 3 12 149 12.6 74 5 3## 4 18 313 11.5 62 5 4## 5 NA NA 14.3 56 5 5## 6 28 NA 14.9 66 5 6lapply(airquality, mean, na.rm = TRUE)## $Ozone## [1] 42.12931## ## $Solar.R## [1] 185.9315## ## $Wind## [1] 9.957516## ## $Temp## [1] 77.88235## ## $Month## [1] 6.993464## ## $Day## [1] 15.80392Simulation again
lapply(seq(1, 5, 0.2), rnorm, n = 10, mean = 0)## [[1]]## [1] -0.02516264 -0.16367334 0.37005975 -0.38082454 0.65295237 2.06134181 -1.79664494## [8] 0.58407712 -0.72275312 -0.62916466## ## [[2]]## [1] -2.1794473 -0.3111469 0.4015587 -1.7126011 2.3263539 -0.9114363 -2.7345314## [8] -0.1368609 2.8222280 1.9155850## ## [[3]]## [1] 1.7884237 1.1045592 0.6460515 -0.6132968 -2.1109298 -3.1121246 -1.6501414## [8] -2.4958643 -1.3830868 1.0198842## ## [[4]]## [1] -1.4154959 -2.4615063 -1.6710007 -2.7490179 1.2860121 -2.4028595 -0.2327985## [8] 0.9271338 1.9224409 3.0302573## ## [[5]]## [1] -3.1684074 1.6641842 -1.0017759 -0.3250514 2.6053925 -1.0928366 1.2228524## [8] -0.1684038 -0.8821553 2.5391869## ## [[6]]## [1] -0.4491476 -0.4249910 1.3927569 1.8303650 -1.8467486 2.2937465 -1.2717301## [8] -1.7728866 -4.6662734 -0.2909816## ## [[7]]## [1] 0.6973209 -1.5564340 2.7327422 1.3643348 0.2197867 3.9769477 -3.3053460## [8] 0.6284090 1.8605553 -2.1897538## ## [[8]]## [1] -0.6164499 -0.1340545 -1.0680126 0.1672682 -0.3712121 -1.9950323 1.8277064## [8] -1.3836166 -1.5032837 1.1552048## ## [[9]]## [1] 4.40770482 -4.57918836 0.51483384 1.03310766 0.07598629 6.65671081 3.26853205## [8] -1.38979798 -1.62559131 2.37600659## ## [[10]]## [1] 2.82015870 2.01401711 -1.69319265 1.50935234 -0.21512648 5.17977477 -2.39374114## [8] 0.09138443 -2.87016655 -2.75029741## ## [[11]]## [1] 0.01230587 -0.70028153 -1.49666466 4.64913889 0.26249075 3.95610339 -2.94367236## [8] -0.73686776 -4.21180151 4.32267944## ## [[12]]## [1] -3.14035197 4.71758369 -3.17183118 -0.30239150 -9.20045339 -0.78997152 0.04718235## [8] -6.14108065 -0.92100398 -1.10923983## ## [[13]]## [1] -6.2546012 3.0552024 -4.1237070 -0.7444784 1.9185117 -1.7864769 2.5308724## [8] 0.4385380 5.0601325 -2.2531186## ## [[14]]## [1] -4.1783580 1.2915872 -0.7014470 -1.0630152 1.7879055 1.7456860 0.0676242## [8] 2.2851884 2.7159987 3.0009205## ## [[15]]## [1] 3.6698929 4.9167439 -0.5188939 -1.6725270 -4.6636789 -0.9030817 -3.5220610## [8] 1.5626944 -0.7556854 -2.1183086## ## [[16]]## [1] -3.908628 0.242941 -2.388918 -5.035795 -5.640189 4.405216 -2.708968 -3.048694## [9] -1.166994 -2.300754## ## [[17]]## [1] -1.8645558 -1.3127959 -2.5326186 -4.5945258 3.0017660 -0.4570115 -6.0639513## [8] 3.3857177 -7.3073073 -1.6855453## ## [[18]]## [1] -1.265363 -4.128993 1.265735 -6.623765 6.684907 1.616601 7.479395 2.834467## [9] -7.426325 2.849642## ## [[19]]## [1] 2.064453 4.720990 4.944900 2.108224 2.905299 -2.670145 7.287284 -8.114368## [9] -8.650861 -5.941908## ## [[20]]## [1] 4.36641814 -5.31722727 -1.84379460 0.39712720 -2.32263588 -10.00675740## [7] 5.60441743 -0.36876370 2.54602270 0.02356222## ## [[21]]## [1] -2.6511571 7.5743333 4.0772982 -7.5326093 -5.7859009 6.5077747 -4.5282039## [8] 0.0778174 -7.1400260 3.4398985Mimic dplyr::group_by
by_cyl <- split(mtcars, mtcars$cyl)str(by_cyl)## List of 3## $ 4:'data.frame': 11 obs. of 11 variables:## ..$ mpg : num [1:11] 22.8 24.4 22.8 32.4 30.4 33.9 21.5 27.3 26 30.4 ...## ..$ cyl : num [1:11] 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 ...## ..$ disp: num [1:11] 108 146.7 140.8 78.7 75.7 ...## ..$ hp : num [1:11] 93 62 95 66 52 65 97 66 91 113 ...## ..$ drat: num [1:11] 3.85 3.69 3.92 4.08 4.93 4.22 3.7 4.08 4.43 3.77 ...## ..$ wt : num [1:11] 2.32 3.19 3.15 2.2 1.61 ...## ..$ qsec: num [1:11] 18.6 20 22.9 19.5 18.5 ...## ..$ vs : num [1:11] 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 ...## ..$ am : num [1:11] 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 ...## ..$ gear: num [1:11] 4 4 4 4 4 4 3 4 5 5 ...## ..$ carb: num [1:11] 1 2 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 2 ...## $ 6:'data.frame': 7 obs. of 11 variables:## ..$ mpg : num [1:7] 21 21 21.4 18.1 19.2 17.8 19.7## ..$ cyl : num [1:7] 6 6 6 6 6 6 6## ..$ disp: num [1:7] 160 160 258 225 168 ...## ..$ hp : num [1:7] 110 110 110 105 123 123 175## ..$ drat: num [1:7] 3.9 3.9 3.08 2.76 3.92 3.92 3.62## ..$ wt : num [1:7] 2.62 2.88 3.21 3.46 3.44 ...## ..$ qsec: num [1:7] 16.5 17 19.4 20.2 18.3 ...## ..$ vs : num [1:7] 0 0 1 1 1 1 0## ..$ am : num [1:7] 1 1 0 0 0 0 1## ..$ gear: num [1:7] 4 4 3 3 4 4 5## ..$ carb: num [1:7] 4 4 1 1 4 4 6## $ 8:'data.frame': 14 obs. of 11 variables:## ..$ mpg : num [1:14] 18.7 14.3 16.4 17.3 15.2 10.4 10.4 14.7 15.5 15.2 ...## ..$ cyl : num [1:14] 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 ...## ..$ disp: num [1:14] 360 360 276 276 276 ...## ..$ hp : num [1:14] 175 245 180 180 180 205 215 230 150 150 ...## ..$ drat: num [1:14] 3.15 3.21 3.07 3.07 3.07 2.93 3 3.23 2.76 3.15 ...## ..$ wt : num [1:14] 3.44 3.57 4.07 3.73 3.78 ...## ..$ qsec: num [1:14] 17 15.8 17.4 17.6 18 ...## ..$ vs : num [1:14] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...## ..$ am : num [1:14] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...## ..$ gear: num [1:14] 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 ...## ..$ carb: num [1:14] 2 4 3 3 3 4 4 4 2 2 ...## $`4`
## ## $`6`
## ## $`8`
## # A tibble: 344 x 8## species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g sex ## <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <fct> ## 1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 181 3750 male ## 2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.400 186 3800 female## 3 Adelie Torgersen 40.300 18 195 3250 female## 4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA NA <NA> ## 5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 193 3450 female## 6 Adelie Torgersen 39.300 20.6 190 3650 male ## 7 Adelie Torgersen 38.9 17.8 181 3625 female## 8 Adelie Torgersen 39.2 19.6 195 4675 male ## 9 Adelie Torgersen 34.1 18.1 193 3475 <NA> ## 10 Adelie Torgersen 42 20.2 190 4250 <NA> ## # … with 334 more rows, and 1 more variable: year <int>Saving
You can extend this example further by saving the plot outputs to an object, then looping through that object to save the plots to disk.
Using functionals, this would require parallel iterations, which we'll cover later (need to loop through plots and a file name)
Could extend it fairly easily with a
forloop
Saving w/for loop
Save plots to an object (list)
plots <- lapply(by_cyl, function(x) { ggplot(x, aes(disp, mpg)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth()})Specify file names/directory
#dir.create(here::here("plots")) filenames <- here::here("plots", paste0("cyl", names(by_cyl), ".png"))filenames## [1] "/Users/daniel/Teaching/data_sci_specialization/2020-21/c3-fp-2021/plots/cyl4.png"## [2] "/Users/daniel/Teaching/data_sci_specialization/2020-21/c3-fp-2021/plots/cyl6.png"## [3] "/Users/daniel/Teaching/data_sci_specialization/2020-21/c3-fp-2021/plots/cyl8.png"Variants of lapply
sapplyWill try to simplify the output, if possible. Otherwise it will return a list.
Fine for interactive work, but I strongly recommend against it if writing a function (difficult to predict the output)
vapplyStrict - you specify the output
Use if writing functions (or just always stick with
lapply), or consider jumping to{purrr}(next week)
Examples
Our simulation
sim_s <- sapply(seq(1, 5, by = 0.2), function(x) { rnorm(10, 0, x)})class(sim_s)## [1] "matrix" "array"dim(sim_s)## [1] 10 21sim_s## [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6] [,7]## [1,] -2.939773695 -0.38696441 -2.0067288 -0.6857975 0.26119194 -2.6882602 -5.3073906## [2,] 0.002415809 -1.60656089 -1.4772590 -1.0498872 -4.39616038 -3.0463115 -0.6903443## [3,] 0.509665571 0.82578723 -1.0263566 1.5350309 1.04457363 -0.8439364 3.6517332## [4,] -1.084720001 0.08553678 0.2952702 2.4896842 1.17909360 2.7218489 0.2880968## [5,] 0.704832977 2.62770283 -1.3984890 -1.6652743 -0.54811591 3.5075897 2.4109551## [6,] 0.330976350 -1.38924912 1.5089905 1.4889159 -1.27362282 3.1367295 1.0765501## [7,] 0.976327473 1.41802568 -1.6785641 -0.1207135 3.54882963 2.5935111 -1.7136026## [8,] -0.843339880 -0.63284203 0.3032918 -3.1475126 -0.16199763 -0.4751925 3.8358306## [9,] -0.970579905 -1.74795361 0.2003218 -1.2094458 -0.02523105 -2.4483003 -0.1724520## [10,] -1.771531349 0.68756084 -1.4920501 0.7378387 -2.02222249 -0.6556254 -2.1462183## [,8] [,9] [,10] [,11] [,12] [,13] [,14]## [1,] 0.1695836 -1.1734150 -3.768222 -6.10501062 5.4168761 -3.3350679 -4.8069314## [2,] -3.6446389 2.4052205 2.894263 6.06404098 2.0548247 3.6963109 1.4332445## [3,] 2.0730697 -0.5164141 -2.272974 3.01792046 4.1031457 0.4737119 -0.4017125## [4,] 1.2037641 3.1066126 5.044831 2.45137080 0.4497503 -1.3133251 2.4326781## [5,] -0.8514752 1.2884162 4.960317 -1.99196485 -3.5600086 3.8201904 -2.8389526## [6,] -1.1722293 -5.8373967 -4.073136 -0.03384369 -1.0869663 -2.5834752 -0.3131508## [7,] 2.2471055 -3.4719655 -2.367832 1.85903177 -5.3272468 3.9064610 4.9762224## [8,] -2.5497801 3.3352155 -3.501343 -3.84371623 2.9723256 -2.8644193 0.6065646## [9,] -2.3611701 1.7960694 1.868407 -0.37278398 4.5338459 1.3308054 2.9634874## [10,] 1.0181949 -2.5143629 -3.614155 0.52722496 -0.2007065 3.0306826 -0.7952206## [,15] [,16] [,17] [,18] [,19] [,20] [,21]## [1,] -3.91168829 -0.7117919 8.3144599 0.73152216 5.361125 0.7562907 -4.721494## [2,] -0.04151763 -1.7039254 3.3465371 -5.58623589 10.287085 4.4802659 -3.829450## [3,] -4.65496639 3.9866351 -7.1789600 10.33777061 1.390419 1.4535757 -4.768896## [4,] -9.86522328 2.9106428 -6.9874086 -6.21282379 -4.795530 -9.3895211 -1.990022## [5,] 4.44266585 -6.9065224 2.0626601 -0.07463057 -4.524295 1.6969762 -1.556085## [6,] -4.13025350 1.4135940 -0.7310330 -2.39500515 9.226305 2.1620377 3.980464## [7,] -6.93911545 2.9072547 4.0374204 7.92049427 -9.524629 3.1658442 4.932142## [8,] 3.78207087 2.6730439 1.2340720 4.45033678 14.056415 -4.9508195 -3.972658## [9,] -0.04507477 -9.6972692 0.3401973 -2.48035285 -1.202213 -11.3809098 -1.544090## [10,] -2.27858790 -0.9414297 0.7713797 0.90385150 -2.090209 -1.5579663 1.807224head(penguins)## # A tibble: 6 x 8## species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g sex ## <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <fct> ## 1 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 181 3750 male ## 2 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.400 186 3800 female## 3 Adelie Torgersen 40.300 18 195 3250 female## 4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA NA NA <NA> ## 5 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 193 3450 female## 6 Adelie Torgersen 39.300 20.6 190 3650 male ## # … with 1 more variable: year <int>head( penguins[ ,sapply(penguins, is.double)] )## # A tibble: 6 x 2## bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm## <dbl> <dbl>## 1 39.1 18.7 ## 2 39.5 17.400## 3 40.300 18 ## 4 NA NA ## 5 36.7 19.3 ## 6 39.300 20.6head( penguins[ ,!sapply(penguins, is.double)] )## # A tibble: 6 x 6## species island flipper_length_mm body_mass_g sex year## <fct> <fct> <int> <int> <fct> <int>## 1 Adelie Torgersen 181 3750 male 2007## 2 Adelie Torgersen 186 3800 female 2007## 3 Adelie Torgersen 195 3250 female 2007## 4 Adelie Torgersen NA NA <NA> 2007## 5 Adelie Torgersen 193 3450 female 2007## 6 Adelie Torgersen 190 3650 male 2007vapply(mtcars, mean, FUN.VALUE = double(1))## mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs ## 20.090625 6.187500 230.721875 146.687500 3.596563 3.217250 17.848750 0.437500 ## am gear carb ## 0.406250 3.687500 2.812500vapply(penguins, is.double, FUN.VALUE = character(1))## Error in vapply(penguins, is.double, FUN.VALUE = character(1)): values must be type 'character',## but FUN(X[[1]]) result is type 'logical'vapply(penguins, is.double, FUN.VALUE = logical(1))## species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm ## FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE ## flipper_length_mm body_mass_g sex year ## FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSESummary
The
lapplyfamily of functions help put the focus on a given function, and what values are being looped through the functionlapplywill always return a listsapplywill try to simplify, which is problematic for programming, but fine for interactive workvapplyis strict, and will only return the type specified

